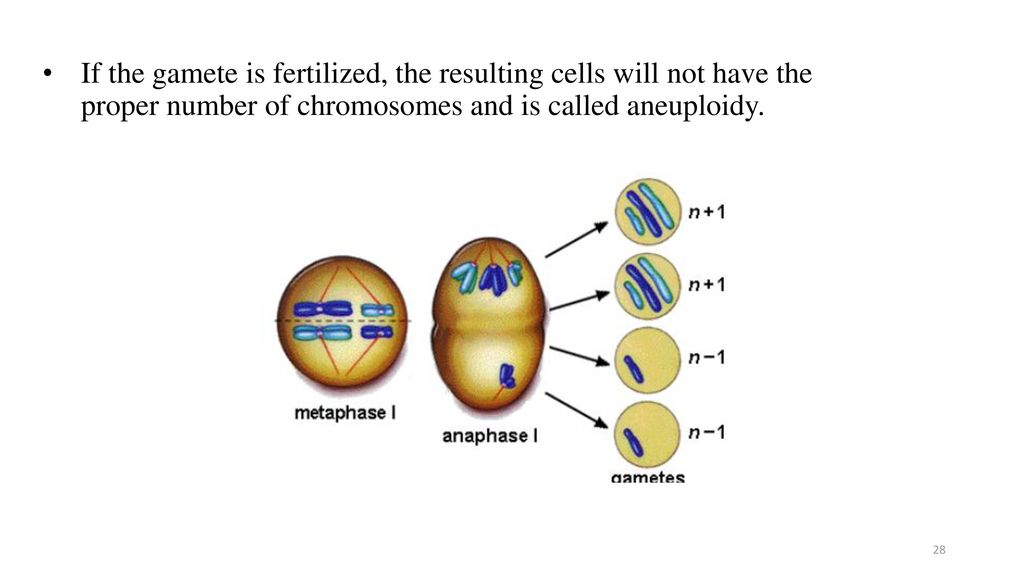
Aneuploidy Cells Losing Their Balance Biology Diagrams The cell cycle is a complex sequence of events through which a cell duplicates its contents and divides, and involves many regulatory proteins for proper cellular reproduction, including cyclin proteins and cyclin-dependent kinases, oncogenes and tumor-suppressor genes, and mitotic checkpoint protei …
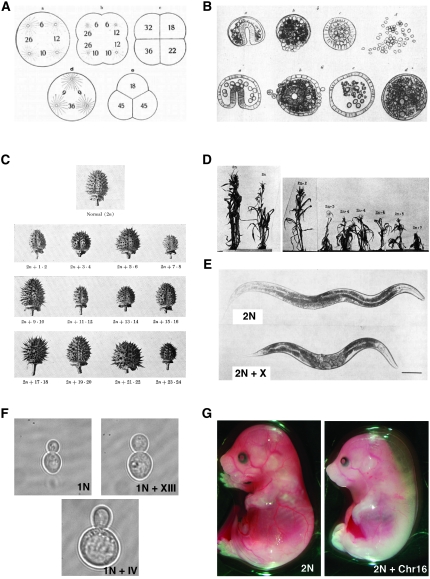
Here, p53-dependent cell cycle arrest would be induced after structural, rather than numerical, aneuploidy and only once a critical threshold of DNA damage is reached.

segregation triggers cell cycle arrest through a ... Biology Diagrams
The cell cycle is a complex sequence of events through which a cell duplicates its contents and divides, and Cell-cycle Checkpoints and Aneuploidy on the Path to Cancer ELIZABETH S. WENZEL and AMARESHWAR T. K. SINGH Department of Biology, Division of Natural and Social Sciences, Carthage College, Kenosha, WI, U.S.A.
Keywords: Cell-cycle checkpoints, cancer, regulation, cyclins, cyclin-dependent kinases, aneuploidy, review The cell cycle is a complex sequence of events through which a cell duplicates its contents and divides, resulting in two genetically identical daughter cells. Aneuploidy often confers a proliferative disadvantage with a delay in the G1 and S phases of the cell cycle, probably due to delayed accumulation of cyclins 63,68,70,73,74,75. The proliferation Centrosome duplication is a crucial process ensuring proper cell division, influencing chromosome segregation and overall cellular organization. Errors in this process can lead to aneuploidy or tumorigenesis, highlighting its significance in both normal development and disease. Role In Cell Cycle Progression

Aneuploidy increases resistance to chemotherapeutics by ... Biology Diagrams
Proliferation and cell cycle. As described above, aneuploidy is generally detrimental to cell proliferation when initially induced (8, 23, 30, 143), but this is an advantage for adaptability (144, 145).Fitness benefits are observed in vitro in challenging culture conditions such as serum-free media, hypoxia, or drug treatment (82, 84, 146).Higher aneuploidy correlates with a higher mitotic