Define the term Biotic then give an example Biology Diagrams Detritivores as Primary Consumers: In the detritus food chain, detritivores serve as primary consumers, feeding on dead organic matter or detritus. These detritivores, such as earthworms, insects, or crustaceans, play a vital role in the breakdown of detritus into simpler compounds.

The detritus food chain starts from dead decomposing organic materials. In this article, we will look into the meaning, diagram, implications, and examples of the detritus food chain. We will also discuss the differences between the grazing food chain and the detritus food chain.

Detritivores: Decomposers In The Food Chain Biology Diagrams
Detritus food chain is the type of food chain that starts with dead organic materials. The dead organic substances are decomposed by microorganisms. The organisms that feed on dead organic matter or detritus, are known as detritivores or decomposers. These detritivores are later eaten by predators. In the detritus food chain, the excreted products by one organism is utilized by another

The water-soluble nutrients produced from this leach into the soil and increase the soil mineral content. At the same time, the detritivores are extracting nutrition for their own life cycles, and in doing so, contribute their biomass to the food chain when they are eaten by consumers. Detritivores, organisms that feed on decaying organic matter, play a critical role in ecosystems. They decompose dead organisms and recycle nutrients, occupying a unique trophic level within the food chain. Detritivores are classified as consumers, but their food source sets them apart from other trophic levels. Unlike herbivores, they do not consume living plants, and unlike carnivores, they
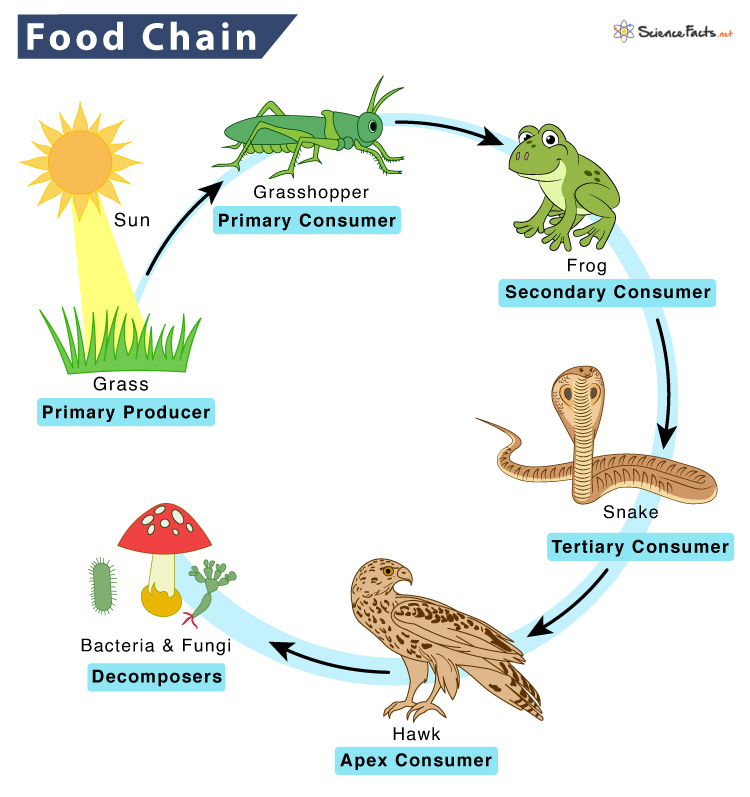
Decomposer food chain: Definition and classification Biology Diagrams
The detrital food chain - this is also known as the decomposer food chain Decomposers, such as bacteria and fungus, break down dead organic matter or dead organic compounds from plants and animals in a detrital food chain, which then transfers to detritivores and finally predators.
