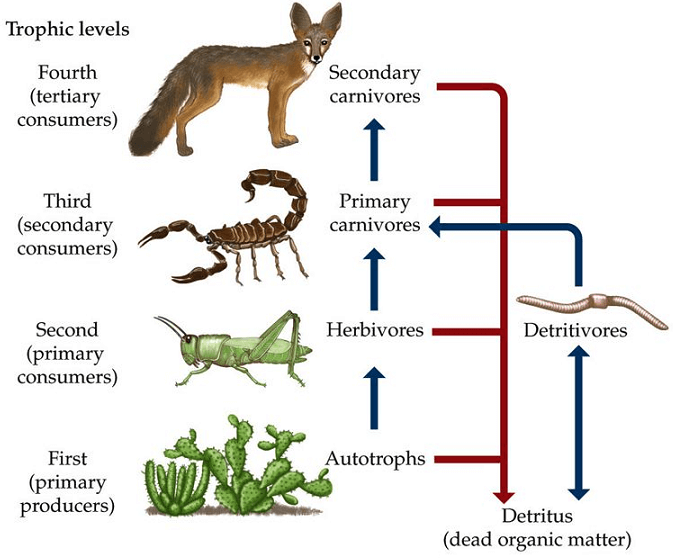
Ecosystems and Food Chains Lesson 1 Biology Diagrams Food Chains. A food chain is a linear sequence of organisms through which nutrients and energy pass as one organism eats another; the levels in the food chain are producers, primary consumers, higher-level consumers, and finally decomposers. These levels are used to describe ecosystem structure and dynamics. There is a single path through a

By studying food chains, ecologists better understand ecosystem dynamics, including the flow of energy, population control, and the impact of human activities on natural habitats. Key Points. Food chains are linear models that illustrate energy transfer from producers to top consumers. Each organism in a food chain contributes to ecosystem balance. Unlike a simple food chain, which follows a linear path, a food web illustrates the interconnectedness of various food chains within an ecosystem. In your backyard, this complex web encompasses everything from producers like plants and algae to consumers like insects, birds, and maybe even a visiting squirrel or two. Producers: The Foundation
9.3: Food Chains and Food Webs Biology Diagrams
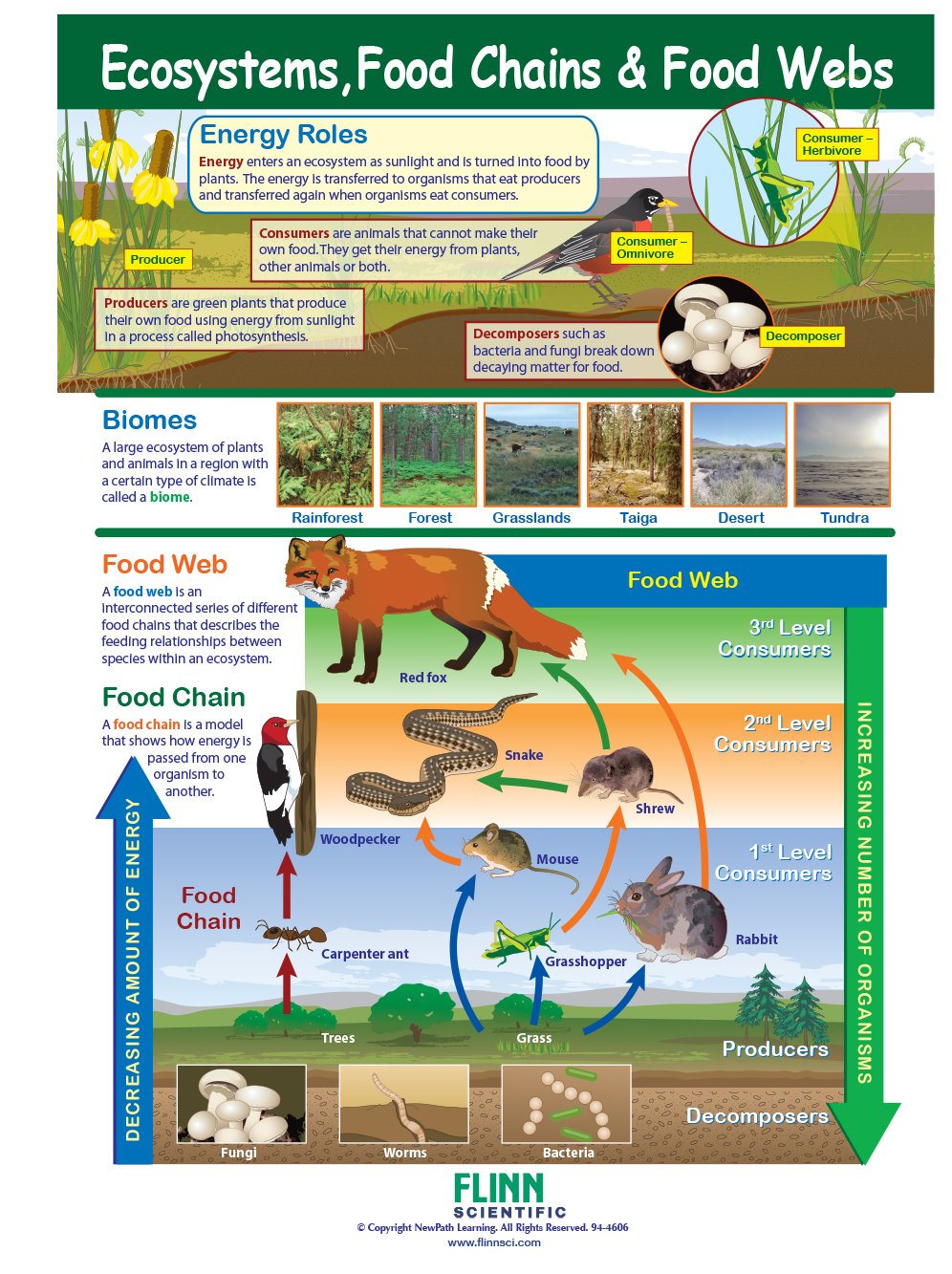
A b i oti c - Non-living features in an ecosystem such as sunlight, water, and minerals in the soil. Hab i tat - The natural home of an animal, plant, or other organism. F ood Chai n: A model that shows how energy flows through living things in an ecosystem. F ood W e b: A system of interconnected and interdependent food chains.
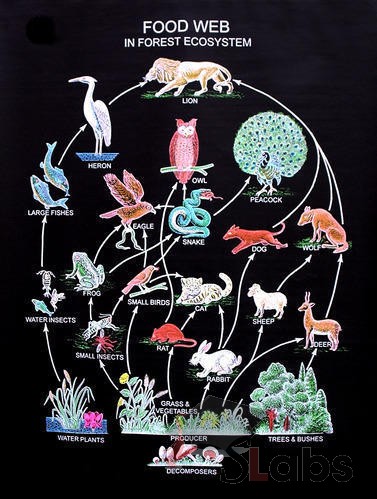
Disrupting the food chain. Like any ecosystem, gardens involve an intricate web of life, from the soil microbes underground to the birds in the trees. Many of the animals and plants we think Idea for Use in the Classroom Introduce food chains and food webs to students and go through vocabulary associated with these concepts. Make sure to include terms that describe an organism by what it feeds on (herbivore, carnivore, and omnivore) and the trophic levels (primary producer, primary consumer, secondary consumer, tertiary consumer, and decomposer). A food web shows how the different trophic levels within various food chains interconnect and how energy flows through them within an ecosystem. Trophic Levels in a Food Web A lion is an example

PDF The Garden Food Chain Biology Diagrams
For example, looking at the food chains and ecosystem niches in my own garden has allowed me to recognize that I should let voles (to give one example) inhabit the space. A Vole's Role in a Garden A food chain describes how living organisms get their food. All organisms, from the most complex to the most simple ones, need food to survive. Living things can be part of multiple food chains and all connected food chains in an ecosystem combine to make a food web.. As shown in the infographic below, a basic food chain is composed of producers, consumers, and decomposers.