Energy Transfer Along A Food Chain Biology Diagrams The food chain starts with producers and ends with decomposers. A food chain diagram shows how energy passes within an ecosystem through organisms eating and being eaten. The diagram of the food chain class 6 and 7 is an important topic in the biology syllabus and is often asked in the examinations. It depicts the sequential transfer of There are basically three different types of food chains in the ecosystem, namely - Grazing food chain (GFC) - This is the normal food chain that we observe in which plants are the producers and the energy flows from the producers to the herbivores (primary consumers), then to carnivores (secondary consumers) and so on. Saprophytic or Detritus food chain (DFC) - In this type of food

Energy flows unidirectionally through trophic levels in a food chain, with energy decreasing at each transfer. Nutrients cycle through each trophic level ensure a constant supply of essential nutrients for life within an ecosystem. Food Chain Diagram. The food chain diagram is given below: Types of Food Chain
transferring energy Biology Diagrams
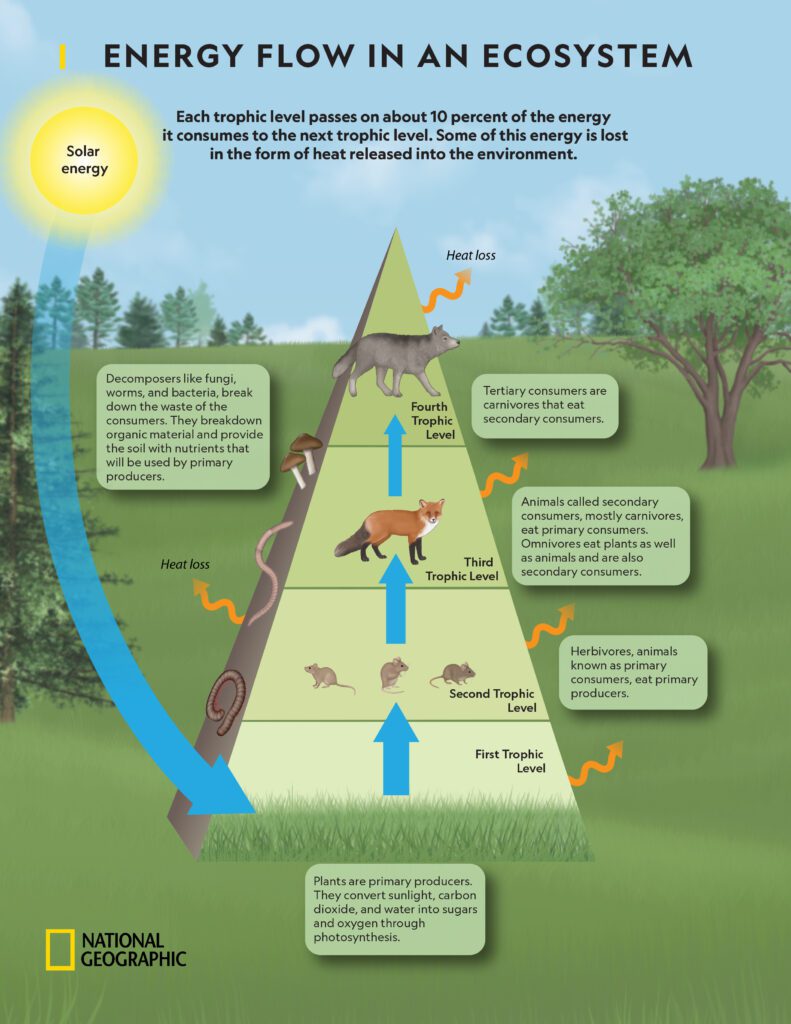
Energy flow in ecosystem is the transfer of energy in a food chain from one living organism to another within an ecosystem. It shows the multiple pathways for energy flow in an ecosystem. Food Web Diagram. For ex: As shown in above diagram, plants are eaten by many herbivores such as Grasshopper, Deer and Mouse for energy. Similarly, Deer The various steps in a food chain at which the transfer of food or energy takes place are called trophic levels. In fact, in a food chain, each step representing an organism forms a trophic level. In simple words, you can say that the term "trophic level" means the "feeding level" of an organism. A food chain close food chain A sequence (usually shown as a diagram) of feeding relationships between organisms, showing which organisms eat what and the movement of energy through trophic levels

It also implies the transfer of food energy from its source in plants through herbivores to carnivores (Krebs 2009). Each food chain is a descriptive diagram including a series of arrows, each A food chain operates on energy transfer across trophic levels, where each level represents a stage in the chain. Producers at the base capture solar energy and convert it into chemical energy, which moves up the chain as each consumer feeds on the one below it. Decomposers break down dead organisms, returning essential nutrients to the
